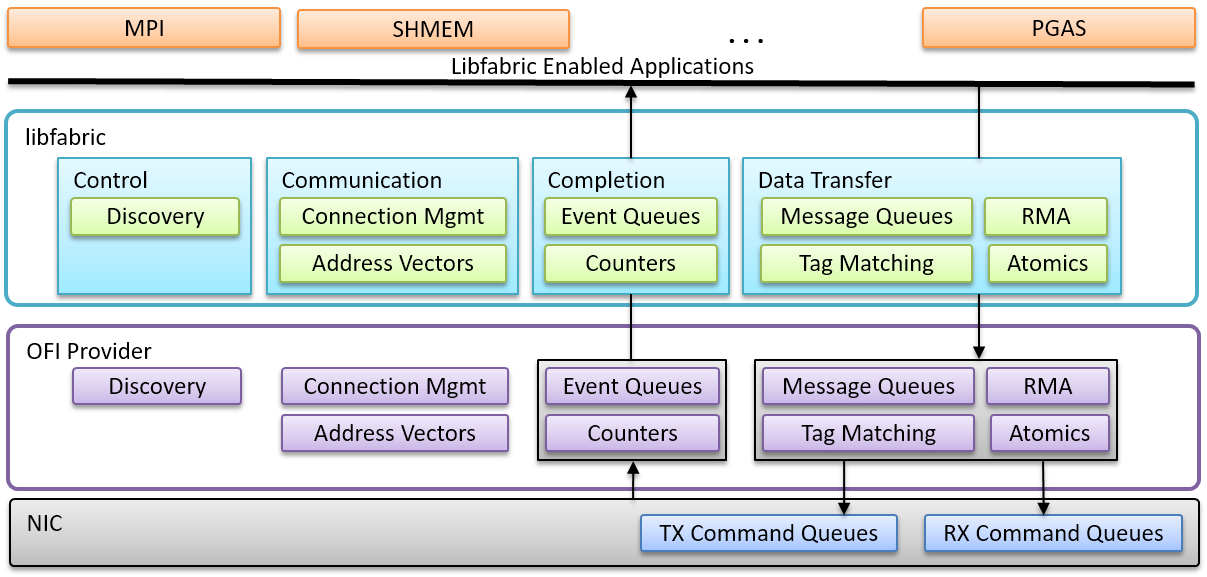
Libfabric¶
Libfabric 简称 OFI,由不希望网络 API 受 InfiniBand 的抽象限制的厂商发起,如 Intel 和 Cicso。它构建在较高的抽象层次,支持 IB Verbs、Sockets、共享内存等。
基础知识¶
整体结构¶
libfabric 整体分为两层:
src中是 Core Service 层,负责提供在 Windows、Linux、OSX 上一致的 API 接口,供上层应用使用prov是 Provider 层,实现具体的底层通信
libfabric 有完善的说明文档,下面总结一些 fi_arch(7) 中的基本知识:
- 通信方式:可以是面向连接的或无连接的,通过概念上类似于套接字的端点(Endpoints)进行通信。
- 数据传输服务:Libfabric 提供了多种数据传输服务,包括消息(messages)、带标签消息(tagged messages)、远程内存访问(RMA)、原子操作(atomics)和集合操作(collectives)。
- 内存注册(Memory Registration):这是一个关键概念,它通过锁定虚拟到物理的内存映射,使网络硬件能够直接访问应用程序数据缓冲区,并通过注册密钥提供安全机制。
- 完成服务(Completion Services):使用完成队列(completion queues)或计数器(counters)报告异步数据传输操作的结果,旨在实现高性能。
- 面向对象设计:该架构遵循面向对象的设计,包含以下关键对象:
- Fabric (fi_fabric):表示一个或多个网络接口的集合。
- Domain (fi_domain):表示一个特定于 Provider 的网络接口(或一组接口)的功能。
- Passive Endpoint (fi_pep):用于监听传入连接请求。
- Active Endpoint (fi_endpoint):用于实际的数据传输。
- Event Queues (fi_eq):用于接收异步事件,如连接请求、错误等。
- Completion Queue (fi_cq):用于报告异步操作的完成状态。
- Memory Region (fi_mr):表示已注册的内存区域。
- Address Vectors (fi_av):用于存储远程端点的地址信息。
-
**通信模式(Communication Model):
Endpoint 类型 对应 FI_EP_MSGReliable-connectedRDMA RC FI_EP_DGRAMUnreliable datagramRDMA UD FI_EP_RDMReliable-unconnectedRDMA RD
以 Verbs Provider 为例,我们应用一下上面的基本概念,官方文档见 fi_verbs(7)。:
-
支持情况:
libfabric 仓库的 README 文件详细说明了现有的各类 Providers。
libfabric 在文档方面比 OpenMPI 和 UCX 做的都好
使用¶
libfabric 有完善的使用教程。我们先总结 fi_setup(7) 中的要点,然后以 fi_pingpong 的源码为例具体分析。
fi_getinfo()获得struct fi_info*链表,包含可用的 fabric service。其中的关键字段:caps表明提供的能力,如传输服务类型等
fi_fabric()创建一个 Providerfi_domain()使用一个网络接口- 主动端点(Active Endpoints)
- 功能:用于执行数据传输,可以是面向连接或无连接的。所有数据传输接口(如消息、标记消息、RMA、原子操作、集合操作)都与主动端点关联。
- 队列:通常有一个发送队列和一个接收队列。发送队列用于发起数据传输(如发送消息、RMA、原子操作),接收队列用于接收传入数据。
- 状态:创建时处于禁用状态。必须先进行配置并绑定到必要的结构(例如完成队列 CQ、事件队列 EQ 和地址向量 AV),然后调用
fi_enable()才能启用,或通过fi_connect()和fi_accept()自动启用。只有启用后才能进行数据传输操作。
- 被动端点(Passive Endpoints)
- 功能:主要用于监听传入的连接请求,不能执行数据传输。
- 类型:仅支持
FI_EP_MSG类型。 - 绑定:必须绑定到事件队列(Event Queue)以报告连接请求。与主动端点不同,被动端点不与域(domain)关联,允许在不同域但同一提供者下监听连接。
- 连接流程:应用程序通过被动端点监听连接请求,接收到
FI_CONNREQ事件后,会为该连接分配一个新的主动端点,并调用fi_accept()接受连接。
根据 pingpong.c 的代码内容,以下是主要流程的函数名及其使用的 fi_ 调用:
-
初始化阶段
- 函数名:
pp_init_fabric- 使用的
fi_调用:fi_fabric: 初始化 Fabric 资源fi_eq_open: 创建事件队列 (EQ)fi_domain: 创建 Domainfi_av_open: 创建地址向量 (AV)fi_cq_open: 创建完成队列 (CQ)fi_endpoint: 创建端点 (EP)fi_enable: 启用端点
- 使用的
- 函数名:
-
控制消息同步
- 函数名:
pp_ctrl_init,pp_ctrl_sync- 使用的
fi_调用:fi_getname: 获取本地地址fi_av_insert: 将地址插入地址向量fi_eq_sread: 从事件队列读取同步事件
- 使用的
- 函数名:
-
数据传输阶段
- 函数名:
pp_tx,pp_rx,pp_inject- 使用的
fi_调用:fi_send/fi_tsend: 发送数据(普通或带标签)fi_recv/fi_trecv: 接收数据(普通或带标签)fi_inject/fi_tinject: 直接注入数据(无需完成通知)fi_cq_read: 从完成队列读取完成事件
- 使用的
- 函数名:
-
性能测试与统计
- 函数名:
pingpong,show_perf- 使用的
fi_调用:fi_gettime_us: 获取时间戳(用于性能统计)fi_cq_readerr: 读取完成队列错误事件
- 使用的
- 函数名:
-
资源释放与清理
- 函数名:
pp_free_res,pp_finalize- 使用的
fi_调用:fi_close: 关闭 Fabric 资源(Fabric、Domain、EQ、CQ、EP 等)fi_shutdown: 关闭端点连接
- 使用的
- 函数名:
-
其他关键函数
- 地址解析与同步:
pp_getaddrinfo: 解析地址(使用getaddrinfo,非fi_调用)pp_exchange_names_connected: 交换地址信息(通过控制消息)
- 错误处理:
pp_process_eq_err: 处理事件队列错误(调用fi_eq_readerr)
- 地址解析与同步:
源码阅读¶
libfabric 版本数宏定义写在 include/rdma/fabric.h 中。
调试¶
环境变量 FI_LOG_LEVEL=debug
类型系统¶
fi_arch(7) 中提到,libfabric 使用 OOP 设计模式。我们来看看它是怎么对各种实体进行建模的。
fid 作为所有类的基类。
Provider¶
本节以 Verbs Provider 为例,通过几个问题引导,探究 Provider 是如何向上层提供通信能力的。
Provider、Fabric 和 Domain¶
所有 Provider 定义为 struct fi_provider 的实例,通过函数指针调用具体操作:
struct fi_provider vrb_prov = {
.name = VERBS_PROV_NAME,
.version = OFI_VERSION_DEF_PROV,
.fi_version = OFI_VERSION_LATEST,
.getinfo = vrb_getinfo,
.fabric = vrb_fabric,
.cleanup = vrb_fini
};
Fabric 创建时,Provider 的选择在 fi_fabric() 中通过字符串匹配完成,获得对应的 fi_provider 结构,转交给 .fabric 成员:
struct ofi_prov {
struct ofi_prov *next;
char *prov_name;
struct fi_provider *provider;
void *dlhandle;
bool hidden;
bool preferred;
};
__attribute__((visibility ("default"),EXTERNALLY_VISIBLE))
int DEFAULT_SYMVER_PRE(fi_fabric)(struct fi_fabric_attr *attr,
struct fid_fabric **fabric, void *context) {
struct ofi_prov *prov;
fi_ini();
prov = ofi_getprov(top_name, strlen(top_name));
ret = prov->provider->fabric(attr, fabric, context);
}
vrb_fabric() 调用 ofi_fabric_init() 进行通用初始化,然后做一些 Vrb 特有的设置:
int vrb_fabric(struct fi_fabric_attr *attr, struct fid_fabric **fabric,
void *context) {
(*fabric)->fid.ops = &vrb_fi_ops;
(*fabric)->ops = &vrb_ops_fabric;
}
static struct fi_ops_fabric vrb_ops_fabric = {
.size = sizeof(struct fi_ops_fabric),
.domain = vrb_domain,
.passive_ep = vrb_passive_ep,
.eq_open = vrb_eq_open,
.wait_open = fi_no_wait_open,
.trywait = vrb_trywait
};
fi_domain() 直接将操作转交给 fabric->ops->domain(),在上面我们看到这就是 vrb_domain()。它调用 ofi_domain_init() 进行通用初始化,然后做一些 Vrb 特有的设置。对于不同的传输类型,这里有重要的区分:
- 如果 EP 类型为 MSG(RDMA RC)且设备支持 XRC,则进一步转交给
verbs_domain_xrc.c中的函数进行处理。 - Domain 层的 ops 根据 EP 类型不同。
static int
vrb_domain(struct fid_fabric *fabric, struct fi_info *info,
struct fid_domain **domain, void *context) {
ret = ofi_domain_init(fabric, info, &_domain->util_domain, context,
OFI_LOCK_MUTEX);
ret = vrb_open_device_by_name(_domain, info->domain_attr->name);
switch (_domain->ep_type) {
case FI_EP_DGRAM:
_domain->util_domain.domain_fid.ops = &vrb_dgram_domain_ops;
case FI_EP_MSG:
if (_domain->ext_flags & VRB_USE_XRC) {
ret = vrb_domain_xrc_init(_domain);
}
_domain->util_domain.domain_fid.ops = &vrb_msg_domain_ops;
}
ret = vrb_init_progress(&_domain->progress, _domain->info);
*domain = &_domain->util_domain.domain_fid;
}
static int vrb_open_device_by_name(struct vrb_domain *domain, const char *name) {
dev_list = rdma_get_devices(NULL);
const char *rdma_name = ibv_get_device_name(dev_list[i]->device);
}
static struct fi_ops_domain vrb_msg_domain_ops = {
.size = sizeof(struct fi_ops_domain),
.av_open = fi_no_av_open,
.cq_open = vrb_cq_open,
.endpoint = vrb_open_ep,
.scalable_ep = fi_no_scalable_ep,
.cntr_open = fi_no_cntr_open,
.poll_open = fi_no_poll_open,
.stx_ctx = fi_no_stx_context,
.srx_ctx = vrb_srq_context,
.query_atomic = vrb_query_atomic,
.query_collective = fi_no_query_collective,
};
Getinfo¶
众所周知,Verbs 是一套通用的 API,而底层设备能支持的功能可能是受限的。
调用链:fi_getinfo -> prov->provider->getinfo -> vrb_get_info() -> vrb_get_match_infos(raw_info: vrb_util_prov.info) -> vrb_get_matching_info(verbs_info: raw_info) -> check_info: verbs:info。
其中,设备列表的传递:
-
verbs_init.c中定义两个全局链表 -
vrb_get_info()vrb_init_info()调用rdma_get_devices()获取设备列表,初始化上面两个链表- 两个链表传入
vrb_get_match_infos()
关于 Verbs,主要通过下面三个函数查询支持的功能:
static int vrb_get_device_attrs(struct ibv_context *ctx,
struct fi_info *info, uint32_t protocol) {
ret = ibv_query_device(ctx, &device_attr);
ret = vrb_get_qp_cap(ctx, info, protocol);
ret = ibv_query_port(ctx, port_num, &port_attr);
}
Endpoint 的创建和启用(建链)¶
先看数据结构,struct vrb_ep、struct util_ep、struct fid_ep 三级结构层层向上:
struct fid_ep {
struct fid fid;
struct fi_ops_ep *ops;
struct fi_ops_cm *cm;
struct fi_ops_msg *msg;
struct fi_ops_rma *rma;
struct fi_ops_tagged *tagged;
struct fi_ops_atomic *atomic;
struct fi_ops_collective *collective;
};
struct util_ep {
struct fid_ep ep_fid;
struct util_domain *domain;
struct util_av *av;
struct dlist_entry av_entry;
struct util_eq *eq;
/* CQ entries */
struct util_cq *rx_cq;
uint64_t rx_op_flags;
struct util_cq *tx_cq;
uint64_t tx_op_flags;
uint64_t inject_op_flags;
};
struct vrb_ep {
struct util_ep util_ep;
struct ibv_qp *ibv_qp;
struct slist sq_list;
struct slist rq_list;
struct slist prepost_wr_list;
union {
struct rdma_cm_id *id;
struct {
struct ofi_ib_ud_ep_name ep_name;
int service;
};
};
struct vrb_eq *eq;
struct vrb_srx *srx;
struct {
struct ibv_send_wr rma_wr;
struct ibv_send_wr msg_wr;
struct ibv_sge sge;
} *wrs;
struct rdma_conn_param conn_param;
struct vrb_cm_data_hdr *cm_hdr;
void *cm_priv_data;
};
struct vrb_srx {
struct ibv_srq *srq;
};
struct vrb_eq {
struct rdma_event_channel *channel;
};
Endpoint 有多种类型,对应到不同的 QP 种类:
static inline int vrb_get_qp_cap(struct ibv_context *ctx,
struct fi_info *info, uint32_t protocol) {
if (protocol == FI_PROTO_RDMA_CM_IB_XRC)
qp_type = IBV_QPT_XRC_SEND;
else
qp_type = (info->ep_attr->type != FI_EP_DGRAM) ?
IBV_QPT_RC : IBV_QPT_UD;
init_attr.qp_type = qp_type;
qp = ibv_create_qp(pd, &init_attr);
ibv_destroy_qp(qp);
}
fi_endpoint() 直接转交到 domain->ops->endpoint(),在上面我们看到这是 vrb_msg_domain_ops->endpoint,即 vrb_open_ep()。该函数根据 EP 类型,创建具体的资源:
- 消息端点 (FI_EP_MSG):
- 根据是否启用 XRC 设置不同的操作集(如 vrb_msg_xrc_ep_msg_ops 或 vrb_msg_ep_msg_ops)。
- 处理连接请求或被动端点(PEP)的特殊逻辑:
- 如果没有 info->handle,创建 RDMA CM ID。
- 如果是连接请求 (FI_CLASS_CONNREQ),处理 XRC 或普通连接。
- 如果是被动端点 (FI_CLASS_PEP),使用
rdma_resolve_addr()解析地址并绑定。
- 数据报端点 (FI_EP_DGRAM):
- 设置服务名称(从源地址或生成唯一值)。
- 根据线程安全模式设置操作集(如 vrb_dgram_msg_ops 或 vrb_dgram_msg_ops_ts)。
int vrb_open_ep(struct fid_domain *domain, struct fi_info *info,
struct fid_ep **ep_fid, void *context) {
struct vrb_ep *ep;
ep = vrb_alloc_init_ep(info, dom, context);
*ep_fid = &ep->util_ep.ep_fid;
ep->util_ep.ep_fid.fid.ops = &vrb_ep_ops;
ep->util_ep.ep_fid.ops = &vrb_ep_base_ops;
}
static struct fi_ops vrb_ep_ops = {
.size = sizeof(struct fi_ops),
.close = vrb_ep_close,
.bind = vrb_ep_bind,
.control = vrb_ep_control,
.ops_open = vrb_ep_ops_open,
};
梳理一下哪些函数对 vrb_ep 做了修改:
vrb_alloc_init_ep():- 处理 XRC,特化为
struct vrb_xrc_ep - 分配 WR 空间
- 调用
ofi_endpoint_init()通用初始化
- 处理 XRC,特化为
vrb_ep_save_info_attr():处理ep->info_attrvrb_create_ep():创建 RDMA CM ID
fi_enable() 转交为 ep->fid.ops->control(&ep->fid, FI_ENABLE, NULL),即 vrb_ep_ops->control,也即 vrb_ep_control()。根据 command 参数,又被转交到 vrb_ep_enable(ep)。
- 对于 MSG 类型,将使用
rdma_create_qp()建立 RC 连接 - 对于 DGRAM 类型,将使用
ibv_create_qp()建立 UD 连接
static int vrb_ep_enable(struct fid_ep *ep_fid) {
struct ibv_qp_init_attr attr = { 0 };
vrb_msg_ep_get_qp_attr(ep, &attr);
switch (ep->util_ep.type) {
case FI_EP_MSG:
if (ep->srx) {
} else if (domain->ext_flags & VRB_USE_XRC) {
}
if (ep->id->verbs && ep->ibv_qp == NULL) {
ret = rdma_create_qp(ep->id, domain->pd, &attr);
}
case FI_EP_DGRAM:
ret = vrb_create_dgram_ep(domain, ep, &attr);
}
}
// 负责检查 ep 及其父类持有的各项资源,据此设置 QP 参数
void vrb_msg_ep_get_qp_attr(struct vrb_ep *ep,
struct ibv_qp_init_attr *attr) {
attr->qp_type = IBV_QPT_RC;
attr->sq_sig_all = 1;
if (ep->srx) {
attr->srq = ep->srx->srq;
attr->cap.max_recv_wr = 0;
}
}
static int vrb_create_dgram_ep(struct vrb_domain *domain, struct vrb_ep *ep,
struct ibv_qp_init_attr *init_attr) {
init_attr->qp_type = IBV_QPT_UD;
ep->ibv_qp = ibv_create_qp(domain->pd, init_attr);
}
如果支持 XRC(eXtended Reliable Connections),则使用 rdma_create_qp_ex() 建立 XRC 连接,其上层调用路径于上面有所不同,暂未研究。
static int vrb_create_ini_qp(struct vrb_xrc_ep *ep) {
#if VERBS_HAVE_XRC
struct ibv_qp_init_attr_ex attr_ex;
attr_ex.qp_type = IBV_QPT_XRC_SEND;
attr_ex.comp_mask = IBV_QP_INIT_ATTR_PD;
attr_ex.pd = domain->pd;
attr_ex.qp_context = domain;
attr_ex.srq = NULL;
ret = rdma_create_qp_ex(ep->base_ep.id, &attr_ex);
return FI_SUCCESS;
#else /* VERBS_HAVE_XRC */
return -FI_ENOSYS;
#endif /* !VERBS_HAVE_XRC */
}
Active 和 Passive EP¶
先看 Passive EP 的创建过程。fi_passive_ep() -> fabric->ops->passive_ep -> vrb_passive_ep():
int vrb_passive_ep(struct fid_fabric *fabric, struct fi_info *info,
struct fid_pep **pep, void *context) {
ret = rdma_create_id(NULL, &_pep->id, &_pep->pep_fid.fid,
vrb_get_port_space(_pep->info->addr_format));
if (info->src_addr) {
ret = rdma_bind_addr(_pep->id, (struct sockaddr *) info->src_addr);
}
}
如何启用 SRQ?¶
除了 vrb_open_ep() 创建 EP,还有一些函数会修改 EP。其中 vrb_ep_bind() 是唯一给 ep->srx 赋值的地方。调用路径:fi_*ep_bind() -> vrb_ep_ops.bind:
static int vrb_ep_bind(struct fid *fid, struct fid *bfid, uint64_t flags) {
switch (bfid->fclass) {
case FI_CLASS_CQ:
case FI_CLASS_EQ:
case FI_CLASS_SRX_CTX:
if (ep->util_ep.type != FI_EP_MSG)
return -FI_EINVAL;
ep->srx = container_of(bfid, struct vrb_srx, ep_fid.fid);
case FI_CLASS_AV:
}
}
这里的 struct vrb_srx 是怎么来的呢?是通过 fi_srx_context() 创建的,它转交给 domain->ops->srx_ctx,即 vrb_srq_context(),该函数负责调用 ibv_create_srq()。
在源码中,暂时没有看见自动创建 Shareable Receive Context 的地方,推测这里包装为 fi_srx_context() 接口应该是把选择权留给用户了,默认并不启用 SRQ(XRC 除外,未仔细查看是否会自动分配)。