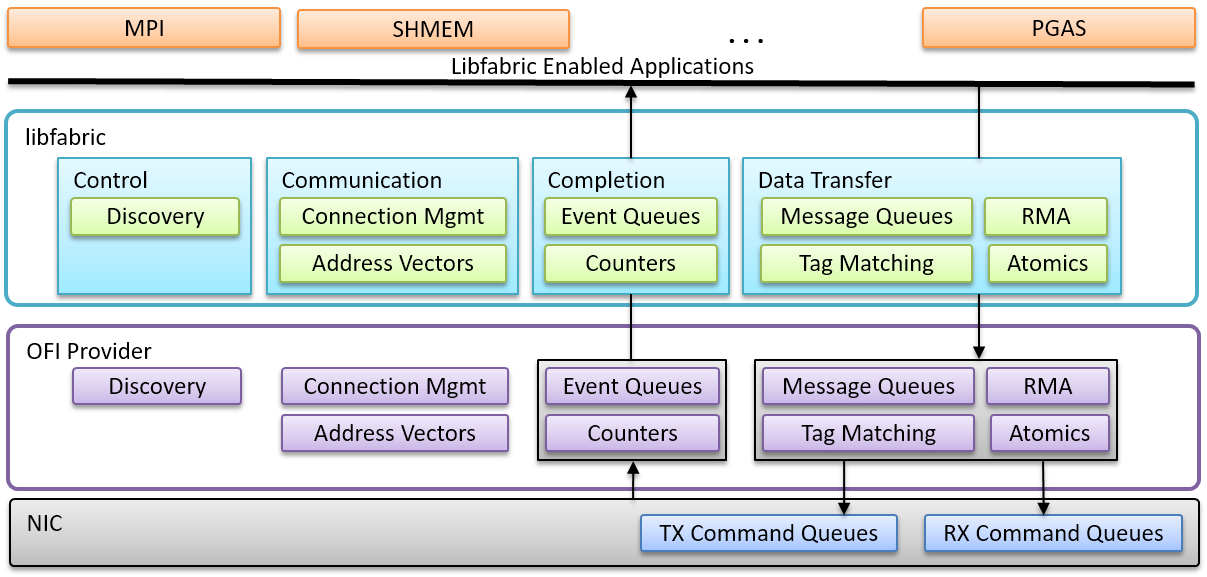
libfabric¶
libfabric 简称 OFI,由不希望网络 API 受 InfiniBand 的抽象限制的厂商发起,如 Intel 和 Cicso。它构建在较高的抽象层次,支持 IB Verbs、Sockets、共享内存等。
基础知识¶
整体结构¶
libfabric 整体分为两层:
src中是 Core Service 层,负责提供和操作系统、底层网卡无关的 API 接口,供上层应用使用prov是 Provider 层,实现具体的底层通信
libfabric 有完善的说明文档,下面总结一些 fi_arch(7) 中的基本知识:
- 通信方式:进程间通过的端点(Endpoints)进行通信,概念上类似于套接字
-
数据传输服务:提供五类通信 API,下面列出部分供读者熟悉 API 命名
fi_msg: fi_recv, fi_recvv, fi_recvmsg, fi_inject fi_rma: fi_read, fi_readv, fi_readmsg, fi_inject_write fi_atomic: fi_atomic, fi_atomicv, fi_atomicmsg, fi_fetch_atomic, fi_compare_atomic fi_tagged: fi_trecv, fi_trecvv, fi_trecvmsg, fi_tinject fi_collective: fi_join_collective, fi_barrier, fi_broadcast, fi_alltoall -
面向对象设计:用户需要操作这些关键对象
- Fabric (
fi_fabric):表示一个或多个网络接口的集合。 - Domain (
fi_domain):表示一个特定于 Provider 的网络接口(或一组接口)的功能。 - Passive Endpoint (
fi_pep):用于监听传入连接请求。 - Active Endpoint (
fi_endpoint):用于实际的数据传输。 - Event Queues (
fi_eq):用于接收异步事件,如连接请求、错误等。 - Completion Queue (
fi_cq):用于报告异步操作的完成状态。 - Memory Region (
fi_mr):表示已注册的内存区域。 - Address Vectors (
fi_av):用于存储远程端点的地址信息。
- Fabric (
-
通信模式(Communication Model):可类比 RDMA 服务类型
Endpoint 类型 类比 FI_EP_MSGReliable-connectedRDMA RC FI_EP_DGRAMUnreliable datagramRDMA UD FI_EP_RDMReliable-unconnectedRDMA RD
以 Verbs Provider 为例,我们应用一下上面的基本概念,官方文档见 fi_verbs(7):
-
支持情况:
libfabric 仓库的 README 文件详细说明了现有的各类 Providers。
libfabric 在文档方面比 OpenMPI 和 UCX 做的都好
编程¶
libfabric 有完善的使用教程。我们先总结 fi_setup(7) 中的要点,然后以 fi_pingpong 的源码为例具体分析。
fi_getinfo()获得struct fi_info*链表,包含可用的 fabric service。其中的关键字段:caps表明提供的能力,如传输服务类型等
fi_fabric()创建一个 Providerfi_domain()使用一个网络接口- 主动端点(Active Endpoints)
- 功能:用于执行数据传输,可以是面向连接或无连接的。所有数据传输接口(如消息、标记消息、RMA、原子操作、集合操作)都与主动端点关联。
- 队列:通常有一个发送队列和一个接收队列。发送队列用于发起数据传输(如发送消息、RMA、原子操作),接收队列用于接收传入数据。
- 状态:创建时处于禁用状态。必须先进行配置并绑定到必要的结构(例如完成队列 CQ、事件队列 EQ 和地址向量 AV),然后调用
fi_enable()才能启用,或通过fi_connect()和fi_accept()自动启用。只有启用后才能进行数据传输操作。
- 被动端点(Passive Endpoints)
- 功能:主要用于监听传入的连接请求,不能执行数据传输。
- 类型:仅支持
FI_EP_MSG类型。 - 绑定:必须绑定到事件队列(Event Queue)以报告连接请求。与主动端点不同,被动端点不与域(domain)关联,允许在不同域但同一提供者下监听连接。
- 连接流程:应用程序通过被动端点监听连接请求,接收到
FI_CONNREQ事件后,会为该连接分配一个新的主动端点,并调用fi_accept()接受连接。
根据 pingpong.c 的代码内容,以下是主要流程的函数名及其使用的 fi_ 调用:
-
初始化阶段
- 函数名:
pp_init_fabric- 使用的
fi_调用:fi_fabric: 初始化 Fabric 资源fi_eq_open: 创建事件队列 (EQ)fi_domain: 创建 Domainfi_av_open: 创建地址向量 (AV)fi_cq_open: 创建完成队列 (CQ)fi_endpoint: 创建端点 (EP)fi_enable: 启用端点
- 使用的
- 函数名:
-
控制消息同步
- 函数名:
pp_ctrl_init,pp_ctrl_sync- 使用的
fi_调用:fi_getname: 获取本地地址fi_av_insert: 将地址插入地址向量fi_eq_sread: 从事件队列读取同步事件
- 使用的
- 函数名:
-
数据传输阶段
- 函数名:
pp_tx,pp_rx,pp_inject- 使用的
fi_调用:fi_send/fi_tsend: 发送数据(普通或带标签)fi_recv/fi_trecv: 接收数据(普通或带标签)fi_inject/fi_tinject: 直接注入数据(无需完成通知)fi_cq_read: 从完成队列读取完成事件
- 使用的
- 函数名:
-
性能测试与统计
- 函数名:
pingpong,show_perf- 使用的
fi_调用:fi_gettime_us: 获取时间戳(用于性能统计)fi_cq_readerr: 读取完成队列错误事件
- 使用的
- 函数名:
-
资源释放与清理
- 函数名:
pp_free_res,pp_finalize- 使用的
fi_调用:fi_close: 关闭 Fabric 资源(Fabric、Domain、EQ、CQ、EP 等)fi_shutdown: 关闭端点连接
- 使用的
- 函数名:
-
其他关键函数
- 地址解析与同步:
pp_getaddrinfo: 解析地址(使用getaddrinfo,非fi_调用)pp_exchange_names_connected: 交换地址信息(通过控制消息)
- 错误处理:
pp_process_eq_err: 处理事件队列错误(调用fi_eq_readerr)
- 地址解析与同步:
运行¶
源码阅读¶
libfabric 版本编号的宏定义写在 include/rdma/fabric.h 中。
类型系统¶
fi_arch(7) 中提到,libfabric 使用 OOP 设计模式。我们来看看它是怎么对各种实体进行建模的。
fid 作为所有类的基类。
fi_ini() 初始化 Provider¶
struct ofi_prov {
struct ofi_prov *next;
char *prov_name;
struct fi_provider *provider;
void *dlhandle;
bool hidden;
bool preferred;
};
// 用于保存所有 provider 的链表
static struct ofi_prov *prov_head, *prov_tail;
fi_ini() 负责加载各 Provider,它在 fi_getinfo() 和 fi_fabric() 中被调用。
fi_ini() 的实现如下:
ofi_ordered_provs_init()
// 遍历预定义的 ordered_prov_names 字符串列表
for (i = 0; i < num_provs; i++)
prov = ofi_alloc_prov(ordered_prov_names[i]);
// 插入预定义的 struct ofi_prov *prov_head 链表
ofi_insert_prov(prov);
ofi_load_dl_prov()
// 搜索预定义的 provider
ofi_find_prov_libs()
// 遍历上面填充的列表
for (prov = prov_head; prov; prov = prov->next)
ofi_reg_dl_prov(lib, false)
dlopen(lib, RTLD_NOW)
inif = dlsym(dlhandle, "fi_prov_ini")
ofi_register_provider((inif)(), dlhandle)
ofi_register_provider(PSM3_INIT, NULL)
//...
其中,fi_prov_ini() 是 External Provider 的入口函数(见 fi_provider(3))。
在预定义的 Provider 中没有该符号定义,将通过分支判断 NULL 直接返回,回到 fi_ini() 中由 ofi_register_provider() 完成。预定义的 Provider 的入口函数由宏定义为 <provider>_INIT。
#define INI_SIG(name) struct fi_provider* name(void)
#define VERBS_INIT fi_verbs_ini()
#define VERBS_INI INI_SIG(fi_verbs_ini)
VERBS_INI
{
return &vrb_prov;
}
struct fi_provider vrb_prov = {
.name = VERBS_PROV_NAME,
.version = OFI_VERSION_DEF_PROV,
.fi_version = OFI_VERSION_LATEST,
.getinfo = vrb_getinfo,
.fabric = vrb_fabric,
.cleanup = vrb_fini
};
fi_getinfo() 获取设备信息¶
struct fi_info {
struct fi_info *next;
uint64_t caps;
uint64_t mode;
uint32_t addr_format;
size_t src_addrlen;
size_t dest_addrlen;
void *src_addr;
void *dest_addr;
fid_t handle;
struct fi_tx_attr *tx_attr;
struct fi_rx_attr *rx_attr;
struct fi_ep_attr *ep_attr;
struct fi_domain_attr *domain_attr;
struct fi_fabric_attr *fabric_attr;
struct fid_nic *nic;
};
fabric_attr将用于调用fi_fabric()
本质上是调用各个 Provider 的 getinfo():
fi_getinfo(FI_VERSION(FI_MAJOR_VERSION, FI_MINOR_VERSION), NULL, NULL, flags, hints, info)
for (prov = prov_head; prov; prov = prov->next)
prov->provider->getinfo(version, node, service, flags, hints, &cur);
以 Verbs Provider 为例,vrb_getinfo() 实现如下:
-
两个全局链表:
vrb_devs和vrb_util_prov.info,分别从getifaddrs()(来自 libc)和rdma_get_devices()(来自 librdmacm)获取 Verbs 设备prov/verbs/src/verbs_init.cDEFINE_LIST(vrb_devs); struct util_prov vrb_util_prov = { .prov = &vrb_prov, .info = NULL, // struct fi_info * .info_lock = &vrb_info_mutex, .flags = 0, };这里的
DEFINE_LIST和内核的双向链表定义和用法相同。
vrb_init_info(&vrb_devs, &vrb_util_prov.info)
// 由 libc 提供
vrb_getifaddrs(verbs_devs)
ofi_getifaddrs(&ifaddr)
getifaddrs(ifaddr)
for (ifa = ifaddr; ifa; ifa = ifa->ifa_next)
// 在该 ifaddrs 上测试 rdma verbs
vrb_ifa_rdma_info(ifa, &dev_name, &rai)
rdma_create_id(NULL, &id, NULL, RDMA_PS_TCP)
rdma_getaddrinfo((char *) name, NULL, &rai_hints, &rai_)
rdma_bind_addr(id, rai_->ai_src_addr)
// 插入 vrb_devs
verbs_devs_add(verbs_devs, dev_name, rai)
// 打印查询到的设备
verbs_devs_print()
// 由 librdmacm 提供
ctx_list = rdma_get_devices(&num_devices)
for (i = 0; i < num_devices; i++)
// 插入 vrb_util_prov.info
vrb_alloc_info(ctx_list[i], &fi, ep_type[j])
// 通过 Verbs API 获取设备信息,并保存到 `info->domain_attr`、`info->tx_attr` 等处
vrb_get_device_attrs(ctx, fi, ep_dom->protocol);
ret = ibv_query_device(ctx, &device_attr);
ret = vrb_get_qp_cap(ctx, info, protocol);
pd = ibv_alloc_pd(ctx);
cq = ibv_create_cq(ctx, 1, NULL, NULL, 0);
qp_type = (info->ep_attr->type != FI_EP_DGRAM) ? IBV_QPT_RC : IBV_QPT_UD;
qp = ibv_create_qp(pd, &init_attr);
ret = ibv_query_port(ctx, port_num, &port_attr);
vrb_get_match_infos(&vrb_devs, version, node, service,
flags, hints, vrb_util_prov.info, info);
// 先尝试 vrb_util_prov.info 来自 librdmacm
vrb_get_matching_info(version, hints, info, raw_info, ofi_is_wildcard_listen_addr(node, service, flags, hints));
struct fi_info *check_info = verbs_info
for (i = 1; check_info; check_info = check_info->next, i++)
// 首先检查 hints
if (hints) vrb_check_hints(version, hints, check_info)
// 然后根据接口类型调用
if ((check_info->ep_attr->type == FI_EP_MSG) && passive)
vrb_get_passive_info()
else
vrb_set_default_info()
// 再尝试 vrb_devs 来自 libc
vrb_handle_sock_addr(verbs_devs, node, service, flags, hints, info)
vrb_handle_ib_ud_addr(node, service, flags, info)
fi_fabric() 创建 Fabric¶
__attribute__((visibility ("default"),EXTERNALLY_VISIBLE))
int DEFAULT_SYMVER_PRE(fi_fabric)(struct fi_fabric_attr *attr,
struct fid_fabric **fabric, void *context) {
struct ofi_prov *prov;
fi_ini();
top_name = attr->prov_name
prov = ofi_getprov(top_name, strlen(top_name));
ret = prov->provider->fabric(attr, fabric, context);
}
ofi_getprov()字符串匹配获得对应的fi_provider实例- 剩余的任务转交给该 Provider 的
.fabric成员
以 Verbs Provider 为例,vrb_fabric() 首先调用 ofi_fabric_init() 进行通用初始化,然后做一些 Verbs 特有的设置,其中最重要的是设置 fabric 的函数表:
int vrb_fabric(struct fi_fabric_attr *attr, struct fid_fabric **fabric,
void *context) {
(*fabric)->fid.ops = &vrb_fi_ops;
(*fabric)->ops = &vrb_ops_fabric;
}
static struct fi_ops_fabric vrb_ops_fabric = {
.size = sizeof(struct fi_ops_fabric),
.domain = vrb_domain,
.passive_ep = vrb_passive_ep,
.eq_open = vrb_eq_open,
.wait_open = fi_no_wait_open,
.trywait = vrb_trywait
};
fi_domain() 启用设备并设置函数表¶
fi_domain() 直接将操作转交给 fabric->ops->domain(),在上面我们看到这就是 vrb_domain()。它调用 ofi_domain_init() 进行通用初始化,然后做一些 Vrb 特有的设置。
不同的 EP 类型从 Domain 开始区分:
- 如果 EP 类型为 MSG(RDMA RC)且设备支持 XRC,则进一步转交给
verbs_domain_xrc.c中的函数进行处理。 - Domain 层的 ops 主要负责 EP 操作,需要根据 EP 类型进行设置。
vrb_domain()
ofi_domain_init(fabric, info, &_domain->util_domain, context, OFI_LOCK_MUTEX);
vrb_open_device_by_name(_domain, info->domain_attr->name);
dev_list = rdma_get_devices(NULL);
const char *rdma_name = ibv_get_device_name(dev_list[i]->device);
switch (_domain->ep_type) {
case FI_EP_DGRAM:
_domain->util_domain.domain_fid.ops = &vrb_dgram_domain_ops;
case FI_EP_MSG:
if (_domain->ext_flags & VRB_USE_XRC) {
ret = vrb_domain_xrc_init(_domain);
}
_domain->util_domain.domain_fid.ops = &vrb_msg_domain_ops;
}
ret = vrb_init_progress(&_domain->progress, _domain->info);
*domain = &_domain->util_domain.domain_fid;
static struct fi_ops_domain vrb_msg_domain_ops = {
.size = sizeof(struct fi_ops_domain),
.av_open = fi_no_av_open,
.cq_open = vrb_cq_open,
.endpoint = vrb_open_ep,
.scalable_ep = fi_no_scalable_ep,
.cntr_open = fi_no_cntr_open,
.poll_open = fi_no_poll_open,
.stx_ctx = fi_no_stx_context,
.srx_ctx = vrb_srq_context,
.query_atomic = vrb_query_atomic,
.query_collective = fi_no_query_collective,
};
fi_endpoint() 建立连接¶
先看数据结构,struct vrb_ep、struct util_ep、struct fid_ep 三级结构层层向上:
struct fid_ep {
struct fid fid;
struct fi_ops_ep *ops;
struct fi_ops_cm *cm;
struct fi_ops_msg *msg;
struct fi_ops_rma *rma;
struct fi_ops_tagged *tagged;
struct fi_ops_atomic *atomic;
struct fi_ops_collective *collective;
};
struct util_ep {
struct fid_ep ep_fid;
struct util_domain *domain;
struct util_av *av;
struct dlist_entry av_entry;
struct util_eq *eq;
/* CQ entries */
struct util_cq *rx_cq;
uint64_t rx_op_flags;
struct util_cq *tx_cq;
uint64_t tx_op_flags;
uint64_t inject_op_flags;
};
struct vrb_ep {
struct util_ep util_ep;
struct ibv_qp *ibv_qp;
struct slist sq_list;
struct slist rq_list;
struct slist prepost_wr_list;
union {
struct rdma_cm_id *id;
struct {
struct ofi_ib_ud_ep_name ep_name;
int service;
};
};
struct vrb_eq *eq;
struct vrb_srx *srx;
struct {
struct ibv_send_wr rma_wr;
struct ibv_send_wr msg_wr;
struct ibv_sge sge;
} *wrs;
struct rdma_conn_param conn_param;
struct vrb_cm_data_hdr *cm_hdr;
void *cm_priv_data;
};
struct vrb_srx {
struct ibv_srq *srq;
};
struct vrb_eq {
struct rdma_event_channel *channel;
};
Endpoint 有多种类型,对应到不同的 QP 种类:
static inline int vrb_get_qp_cap(struct ibv_context *ctx,
struct fi_info *info, uint32_t protocol) {
if (protocol == FI_PROTO_RDMA_CM_IB_XRC)
qp_type = IBV_QPT_XRC_SEND;
else
qp_type = (info->ep_attr->type != FI_EP_DGRAM) ?
IBV_QPT_RC : IBV_QPT_UD;
init_attr.qp_type = qp_type;
qp = ibv_create_qp(pd, &init_attr);
ibv_destroy_qp(qp);
}
fi_endpoint() 直接转交到 domain->ops->endpoint(),在上面我们看到这是 vrb_msg_domain_ops->endpoint,即 vrb_open_ep()。该函数根据 EP 类型,创建具体的资源:
- 消息端点 (FI_EP_MSG):
- 根据是否启用 XRC 设置不同的操作集(如 vrb_msg_xrc_ep_msg_ops 或 vrb_msg_ep_msg_ops)。
- 处理连接请求或被动端点(PEP)的特殊逻辑:
- 如果没有 info->handle,创建 RDMA CM ID。
- 如果是连接请求 (FI_CLASS_CONNREQ),处理 XRC 或普通连接。
- 如果是被动端点 (FI_CLASS_PEP),使用
rdma_resolve_addr()解析地址并绑定。
- 数据报端点 (FI_EP_DGRAM):
- 设置服务名称(从源地址或生成唯一值)。
- 根据线程安全模式设置操作集(如 vrb_dgram_msg_ops 或 vrb_dgram_msg_ops_ts)。
int vrb_open_ep(struct fid_domain *domain, struct fi_info *info,
struct fid_ep **ep_fid, void *context) {
struct vrb_ep *ep;
ep = vrb_alloc_init_ep(info, dom, context);
*ep_fid = &ep->util_ep.ep_fid;
ep->util_ep.ep_fid.fid.ops = &vrb_ep_ops;
ep->util_ep.ep_fid.ops = &vrb_ep_base_ops;
}
static struct fi_ops vrb_ep_ops = {
.size = sizeof(struct fi_ops),
.close = vrb_ep_close,
.bind = vrb_ep_bind,
.control = vrb_ep_control,
.ops_open = vrb_ep_ops_open,
};
梳理一下哪些函数对 vrb_ep 做了修改:
vrb_alloc_init_ep():- 处理 XRC,特化为
struct vrb_xrc_ep - 分配 WR 空间
- 调用
ofi_endpoint_init()通用初始化
- 处理 XRC,特化为
vrb_ep_save_info_attr():处理ep->info_attrvrb_create_ep():创建 RDMA CM ID
fi_enable() 转交为 ep->fid.ops->control(&ep->fid, FI_ENABLE, NULL),即 vrb_ep_ops->control,也即 vrb_ep_control()。根据 command 参数,又被转交到 vrb_ep_enable(ep)。
- 对于 MSG 类型,将使用
rdma_create_qp()建立 RC 连接 - 对于 DGRAM 类型,将使用
ibv_create_qp()建立 UD 连接
static int vrb_ep_enable(struct fid_ep *ep_fid) {
struct ibv_qp_init_attr attr = { 0 };
vrb_msg_ep_get_qp_attr(ep, &attr);
switch (ep->util_ep.type) {
case FI_EP_MSG:
if (ep->srx) {
} else if (domain->ext_flags & VRB_USE_XRC) {
}
if (ep->id->verbs && ep->ibv_qp == NULL) {
ret = rdma_create_qp(ep->id, domain->pd, &attr);
}
case FI_EP_DGRAM:
ret = vrb_create_dgram_ep(domain, ep, &attr);
}
}
// 负责检查 ep 及其父类持有的各项资源,据此设置 QP 参数
void vrb_msg_ep_get_qp_attr(struct vrb_ep *ep,
struct ibv_qp_init_attr *attr) {
attr->qp_type = IBV_QPT_RC;
attr->sq_sig_all = 1;
if (ep->srx) {
attr->srq = ep->srx->srq;
attr->cap.max_recv_wr = 0;
}
}
static int vrb_create_dgram_ep(struct vrb_domain *domain, struct vrb_ep *ep,
struct ibv_qp_init_attr *init_attr) {
init_attr->qp_type = IBV_QPT_UD;
ep->ibv_qp = ibv_create_qp(domain->pd, init_attr);
}
如果支持 XRC(eXtended Reliable Connections),则使用 rdma_create_qp_ex() 建立 XRC 连接,其上层调用路径于上面有所不同,暂未研究。
static int vrb_create_ini_qp(struct vrb_xrc_ep *ep) {
#if VERBS_HAVE_XRC
struct ibv_qp_init_attr_ex attr_ex;
attr_ex.qp_type = IBV_QPT_XRC_SEND;
attr_ex.comp_mask = IBV_QP_INIT_ATTR_PD;
attr_ex.pd = domain->pd;
attr_ex.qp_context = domain;
attr_ex.srq = NULL;
ret = rdma_create_qp_ex(ep->base_ep.id, &attr_ex);
return FI_SUCCESS;
#else /* VERBS_HAVE_XRC */
return -FI_ENOSYS;
#endif /* !VERBS_HAVE_XRC */
}
Active 和 Passive EP¶
先看 Passive EP 的创建过程。fi_passive_ep() -> fabric->ops->passive_ep -> vrb_passive_ep():
int vrb_passive_ep(struct fid_fabric *fabric, struct fi_info *info,
struct fid_pep **pep, void *context) {
ret = rdma_create_id(NULL, &_pep->id, &_pep->pep_fid.fid,
vrb_get_port_space(_pep->info->addr_format));
if (info->src_addr) {
ret = rdma_bind_addr(_pep->id, (struct sockaddr *) info->src_addr);
}
}
如何启用 SRQ?¶
除了 vrb_open_ep() 创建 EP,还有一些函数会修改 EP。其中 vrb_ep_bind() 是唯一给 ep->srx 赋值的地方。调用路径:fi_*ep_bind() -> vrb_ep_ops.bind:
static int vrb_ep_bind(struct fid *fid, struct fid *bfid, uint64_t flags) {
switch (bfid->fclass) {
case FI_CLASS_CQ:
case FI_CLASS_EQ:
case FI_CLASS_SRX_CTX:
if (ep->util_ep.type != FI_EP_MSG)
return -FI_EINVAL;
ep->srx = container_of(bfid, struct vrb_srx, ep_fid.fid);
case FI_CLASS_AV:
}
}
这里的 struct vrb_srx 是怎么来的呢?是通过 fi_srx_context() 创建的,它转交给 domain->ops->srx_ctx,即 vrb_srq_context(),该函数负责调用 ibv_create_srq()。
在源码中,暂时没有看见自动创建 Shareable Receive Context 的地方,推测这里包装为 fi_srx_context() 接口应该是把选择权留给用户了,默认并不启用 SRQ(XRC 除外,未仔细查看是否会自动分配)。
CQ 的创建¶
CQ 在 vrb_msg_ep_get_qp_attr() 中设置:
if (ep->util_ep.tx_cq) {
struct vrb_cq *cq = container_of(ep->util_ep.tx_cq,
struct vrb_cq, util_cq);
attr->cap.max_send_wr = ep->info_attr.tx_size;
attr->cap.max_send_sge = ep->info_attr.tx_iov_limit;
attr->send_cq = cq->cq;
} else {
struct vrb_cq *cq =
container_of(ep->util_ep.rx_cq, struct vrb_cq, util_cq);
attr->send_cq = cq->cq;
}
if (ep->util_ep.rx_cq) {
struct vrb_cq *cq =
container_of(ep->util_ep.rx_cq, struct vrb_cq, util_cq);
attr->cap.max_recv_wr = ep->info_attr.rx_size;
attr->cap.max_recv_sge = ep->info_attr.rx_iov_limit;
attr->recv_cq = cq->cq;
} else {
struct vrb_cq *cq =
container_of(ep->util_ep.tx_cq, struct vrb_cq, util_cq);
attr->recv_cq = cq->cq;
}
优先每个方向使用自己的 CQ,如果不存在则使用对方的 CQ。
层级结构:
struct util_cq {
struct fid_cq cq_fid;
struct util_domain *domain;
}
struct vrb_cq {
struct util_cq util_cq;
struct ibv_comp_channel *channel;
struct ibv_cq *cq;
}
CQ 需由用户创建。以 pingpong 为例:
ct->cq_attr.size = fi->tx_attr->size;
ret = fi_cq_open(ct->domain, &(ct->cq_attr), &(ct->txcq), &(ct->txcq));
if (ret) {
PP_PRINTERR("fi_cq_open", ret);
return ret;
}
ct->cq_attr.size = fi->rx_attr->size;
ret = fi_cq_open(ct->domain, &(ct->cq_attr), &(ct->rxcq), &(ct->rxcq));
if (ret) {
PP_PRINTERR("fi_cq_open", ret);
return ret;
}
CQ 创建过程:
fi_cq_open
vrb_cq_open()
ofi_cq_init(&vrb_prov, domain_fid, &tmp_attr, &cq->util_cq, vrb_cq_progress, context) 注意 vrb_cq_progress
如何使用 event channel¶
从 IB Verbs 逆向找调用:
ibv_poll_cq()
vrb_poll_cq()
vrb_flush_cq()
vrb_cq_trywait():位于 ibv_req_notify_cq 之后
vrb_cq_progress():
vrb_post_send():
以 pingpong.c 中 pp_get_cq_comp() 调用 fi_cq_read() 为例:
fi_cq_read() = struct fi_ops_cq.read = vrb_cq_ops.read = ofi_cq_read()
fi_cq_readfrom() = struct fi_ops_cq.readfrom = vrb_cq_ops.readfrom = vrb_cq_readfrom()
ofi_cq_readfrom(cq_fid, buf, count, src_addr)
cq->progress(cq) = vrb_cq_progress()
vrb_flush_cq()
vrb_poll_cq()
ibv_poll_cq()
ofi_cq_read_entries(cq, buf, count, src_addr)
cq->read_entry(&buf, entry)
util_cq_read_msg()
// 将 entry 中的数据拷贝到 buf
而如果是 Event Channel,则应该调用 fi_cq_sread():
fi_cq_sread() = struct fi_ops_cq.sread = vrb_cq_ops.sread = vrb_cq_sread()
vrb_cq_trywait()
ibv_get_cq_event()
ibv_req_notify_cq()
vrb_flush_cq()
vrb_poll_cq()
ibv_poll_cq()
vrb_poll_events()
poll(_cq->channel->fd)
ibv_get_cq_event()
发送和接收¶
小消息使用 SEND_INLINE:
pp_inject(ct, ct->ep, ct->opts.transfer_size);
pp_post_inject(ct, ep, size + ct->tx_prefix_size)
fi_inject(ep, ct->tx_buf, size, ct->remote_fi_addr) = struct fi_ops_msg.inject = vrb_msg_ep_msg_ops.inject = vrb_msg_ep_inject()
.opcode = IBV_WR_SEND,
.send_flags = IBV_SEND_INLINE,
vrb_send_buf(ep, &wr, buf, len, NULL)
vrb_post_send(ep, wr, 0)
vrb_flush_cq(cq) //当 ep->sq_credits 为 0 时
ibv_post_send(ep->ibv_qp, wr, &bad_wr)
fi_tinject(ep, ct->tx_buf, size, ct->remote_fi_addr, TAG)
= struct fi_ops_tagged.inject // Verbs 不提供
pp_tx(ct, ct->ep, ct->opts.transfer_size)
pp_post_tx(ct, ep, size + ct->tx_prefix_size, ct->tx_ctx_ptr)
fi_send(ep, ct->tx_buf, size, fi_mr_desc(ct->mr), ct->remote_fi_addr, ctx) = struct fi_ops_msg.send = vrb_msg_ep_send()
.opcode = IBV_WR_SEND
.send_flags = (len) <= (ep)->info_attr.inject_size ? IBV_SEND_INLINE : 0
vrb_send_buf(ep, &wr, buf, len, desc)
// 见上文
fi_tsend(ep, ct->tx_buf, size, fi_mr_desc(ct->mr), ct->remote_fi_addr, TAG, ctx)
= struct fi_ops_tagged.tsend // Verbs 不提供
Provider¶
Verbs¶
IFACE 与 DEVICE¶
Verbs 使用 RDMACM 建链,需要使用 rdma_bind_addr() 绑定到相关的网络接口。因此有 vrb_getifaddrs() 来查询接口信息。
使用 getifaddrs(3) 帮助页的示例代码,容易得知返回的内容。
Todo
接下来看该函数如何处理这些接口。
参数配置¶
vrb_msg_ep_get_qp_attr() 从 ep->info_attr 获取了 EP 的 QP 参数,后者由 vrb_ep_save_info_attr() 在 vrb_open_ep() 中将先前 fi_getinfo()(即 vrb_get_device_attrs())拿到的 info 结构体信息存入。
flowchart
n1["vrb_msg_ep_get_qp_attr()"]
n2@{ shape: "hex", label: "ep->info_attr" }
n3@{ shape: "hex", label: "ibv_qp_attr" }
n1 --- n3
n2 --- n1
n4["fi_getinfo()"]
n5["vrb_get_device_attrs()"]
n4 --- n5
n6@{ shape: "hex", label: "info" }
n4 --- n6
n7["vrb_ep_save_info_attr()"]
n6 --- n7
n7 --- n2vrb_get_device_attrs():
ibv_query_device()存入infovrb_get_qp_cap()比较info和全局默认值。后者来自vrb_read_params()。该函数从环境变量中获取参数的具体值,然后覆盖全局变量struct vrb_gl_data vrb_gl_data中的默认值:
static int vrb_read_params(void) {
/* Common parameters */
if (vrb_get_param_int("tx_size", "Default maximum tx context size",
&vrb_gl_data.def_tx_size) ||
(vrb_gl_data.def_tx_size < 0)) {
VRB_WARN(FI_LOG_CORE, "Invalid value of tx_size\n");
return -FI_EINVAL;
}
//...
}
fi_param_* API 支持 Provider 定义、获取参数。Provider 一般会对它包装,例如:
参数格式为 FI_<provider_name>_<param_name>。以 Verbs Provider 为例,支持下列参数:
FI_VERBS_TX_SIZE
FI_VERBS_RX_SIZE
FI_VERBS_TX_IOV_LIMIT
FI_VERBS_RX_IOV_LIMIT
FI_VERBS_INLINE_SIZE
FI_VERBS_MIN_RNR_TIMER
FI_VERBS_USE_ODP
FI_VERBS_PREFER_XRC
FI_VERBS_XRCD_FILENAME
FI_VERBS_CQREAD_BUNCH_SIZE
FI_VERBS_GID_IDX
FI_VERBS_DEVICE_NAME
FI_VERBS_IFACE
FI_VERBS_DGRAM_USE_NAME_SERVER
FI_VERBS_DGRAM_NAME_SERVER_PORT
vrb_read_params():742<info> dmabuf support is disabled
以 FI_VERBS_TX_SIZE 的流向为例:
vrb_read_params(): FI_VERBS_TX_SIZE -> vrb_gl_data.def_tx_size
vrb_set_default_info(): MIN(vrb_gl_data.def_tx_size, info->tx_attr->size) -> info->tx_attr->size
INFO 传递到 vrb_open_ep(),调用 vrb_ep_save_info_attr()
vrb_ep_save_info_attr(): info.tx_attr.size -> ep->info_attr.tx_size
vrb_msg_ep_get_qp_attr(): ep->info_attr.tx_size -> attr->cap.max_send_wr
RxM¶
RxM Provider 能够使用 MSG 端点模拟 RDM 端点,让 OpenMPI 这种只用 RDM 的能够跑在 RC 连接上。让我们看看它是怎么做的。
Provider 种类¶
RxM Provider 将带领我们认识 libfabric 中的 Provider 分类。除了上面的 Verbs Provider 这种实现具体功能的 Provider(称为 Core Provider),还有其他几种 Provider:
这些 Provider 在 fi_getinfo() 中遍历 Provider 时通过下面的特殊分支激活:
if (hints && hints->fabric_attr && hints->fabric_attr->prov_name) {
prov_vec = ofi_split_and_alloc(hints->fabric_attr->prov_name,
";", &count);
}
ofi_layering_ok(prov->provider, prov_vec, count, flags)
初始化¶
rxm_getinfo()
ofix_getinfo(version, node, service, flags, &rxm_util_prov, hints, rxm_info_to_core, rxm_info_to_rxm, info);
ofi_get_core_info(version, node, service, flags, util_prov, hints, base_info, info_to_core, &core_info)
RxM 的三种协议¶
| 协议名称 | 默认上限 | 实现方式 |
|---|---|---|
| Eager | 16K | 直接发送 |
| Segmentation And Reassembly | 128Kb | 分段发送 |
| rendezvous | 无 | 分段发送 |
CQ 创建¶
调用链:
fi_rxm_ini()
// 从环境变量 FI_OFI_RXM_MSG_RX_SIZE 中读取值
fi_param_get_size_t(&rxm_prov, "msg_rx_size", &rxm_msg_rx_size);
rxm_endpoint()
rxm_open_core_res(rxm_ep)
// 获取 core provider(即 Verbs Provider)的 info
ofi_get_core_info(domain->util_domain.fabric->fabric_fid.api_version, NULL, NULL, 0, &rxm_util_prov, ep->rxm_info, NULL, rxm_info_to_core, &ep->msg_info)
ofi_info_to_core(version, util_prov->prov, util_hints, base_attr, info_to_core, &core_hints);
rxm_info_to_core(version, util_hints, base_attr, *core_hints)
core_info->rx_attr->size = rxm_msg_rx_size ? rxm_msg_rx_size : RXM_MSG_RXTX_SIZE;
fi_getinfo(version, node, service, flags | OFI_CORE_PROV_ONLY, core_hints, core_info)
// 打开 core provider 的 ep
rxm_listener_open(ep)
fi_eq_open(rxm_fabric->msg_fabric, &eq_attr, &rxm_ep->msg_eq, rxm_ep);
fi_passive_ep(rxm_fabric->msg_fabric, rxm_ep->msg_info, &rxm_ep->msg_pep, rxm_ep);
fi_pep_bind(rxm_ep->msg_pep, &rxm_ep->msg_eq->fid, 0)
rxm_ep_settings_init(rxm_ep)
assert(rxm_ep->msg_info)
fi_enable() = ep->fid.ops->control(&ep->fid, FI_ENABLE, NULL)
rxm_ep_ctrl(struct fid *fid, int command, void *arg)
rxm_ep_msg_cq_open(ep)
cq_attr.size = rxm_ep->msg_info->rx_attr->size;
if (rxm_ep->msg_info->ep_attr->rx_ctx_cnt != FI_SHARED_CONTEXT)
cq_attr.size *= ofi_universe_size;
cq_attr.size += rxm_ep->msg_info->tx_attr->size * ofi_universe_size;
fi_cq_open(domain->msg_domain, &cq_attr, &rxm_ep->msg_cq, rxm_ep);
vrb_cq_open(struct fid_domain *domain_fid, struct fi_cq_attr *attr, struct fid_cq **cq_fid, void *context)
size = attr->size ? attr->size : VERBS_DEF_CQ_SIZE;
ibv_create_cq(domain->verbs, size, cq, cq->channel, comp_vector);
计算例:若指定 FI_OFI_RXM_MSG_RX_SIZE=128,则 rxm_msg_rx_size 为 128,cq_attr.size = rxm_ep->msg_info->rx_attr->size 为 128。
CQ Size 需要乘比例系数:
- 支持 Shared Context(SRQ)时,比例为
1 + ofi_universe_size - 不支持 Shared Context(SRQ)时,比例为
2 * ofi_universe_size ofi_universe_size默认为 256
通信¶
RxM 提供以下通信接口:
struct fi_ops_msg rxm_msg_ops = {
.size = sizeof(struct fi_ops_msg),
.recv = rxm_recv,
.recvv = rxm_recvv,
.recvmsg = rxm_recvmsg,
.send = rxm_send,
.sendv = rxm_sendv,
.sendmsg = rxm_sendmsg,
.inject = rxm_inject,
.senddata = rxm_senddata,
.injectdata = rxm_injectdata,
};
Send 的所有操作最终都会转交给 rxm_send_common,由其根据消息大小等因素决定具体的通信方式:
rxm_send_common()
if (data_len <= rxm_ep->eager_limit)
rxm_send_eager()
if (rxm_use_direct_send(rxm_ep, count, flags))
rxm_direct_send()
fi_sendv(rxm_conn->msg_ep, send_iov, send_desc, count + 1, 0, tx_buf);
else
fi_send(rxm_conn->msg_ep, &eager_buf->pkt, total_len, eager_buf->hdr.desc, 0, eager_buf)
rxm_ep_do_progress()
fi_cq_read(rxm_ep->msg_cq, &comp, 32)
// 见 verbs CQ 部分
rxm_ep->handle_comp(rxm_ep, &comp[i]) = rxm_handle_comp()
else if (data_len <= rxm_ep->sar_limit)
rxm_send_sar()
else
rxm_send_rndv()
if(pkt_size <= rxm_ep->inject_limit)
fi_inject(rxm_conn->msg_ep, &tx_buf->pkt, pkt_size, 0);
else
fi_send(rxm_conn->msg_ep, &tx_buf->pkt, pkt_size, tx_buf->hdr.desc, 0, tx_buf);
Poll CQ¶
// 如果支持 FI_COLLECTIVE,则会多一层包装处理
rxm_ep_progress_coll()
rxm_ep_progress()
rxm_ep_do_progress()
// 见上文
coll_ep->progress()
API 层¶
libfabric 自身的代码位于 src 下。这部分 API 采用宏导出符号,因此 IDE 可能难以解析到函数定义的位置: